Defining epigenetic mechanisms that regulate X-chromosome inactivation in the immune system and contribute to sex bias in infectious and autoimmune disease.
Anguera Laboratory
Our laboratory investigates X-chromosome Inactivation, and how this epigenetic process contributes to female-bias with autoimmunity & immune responses.
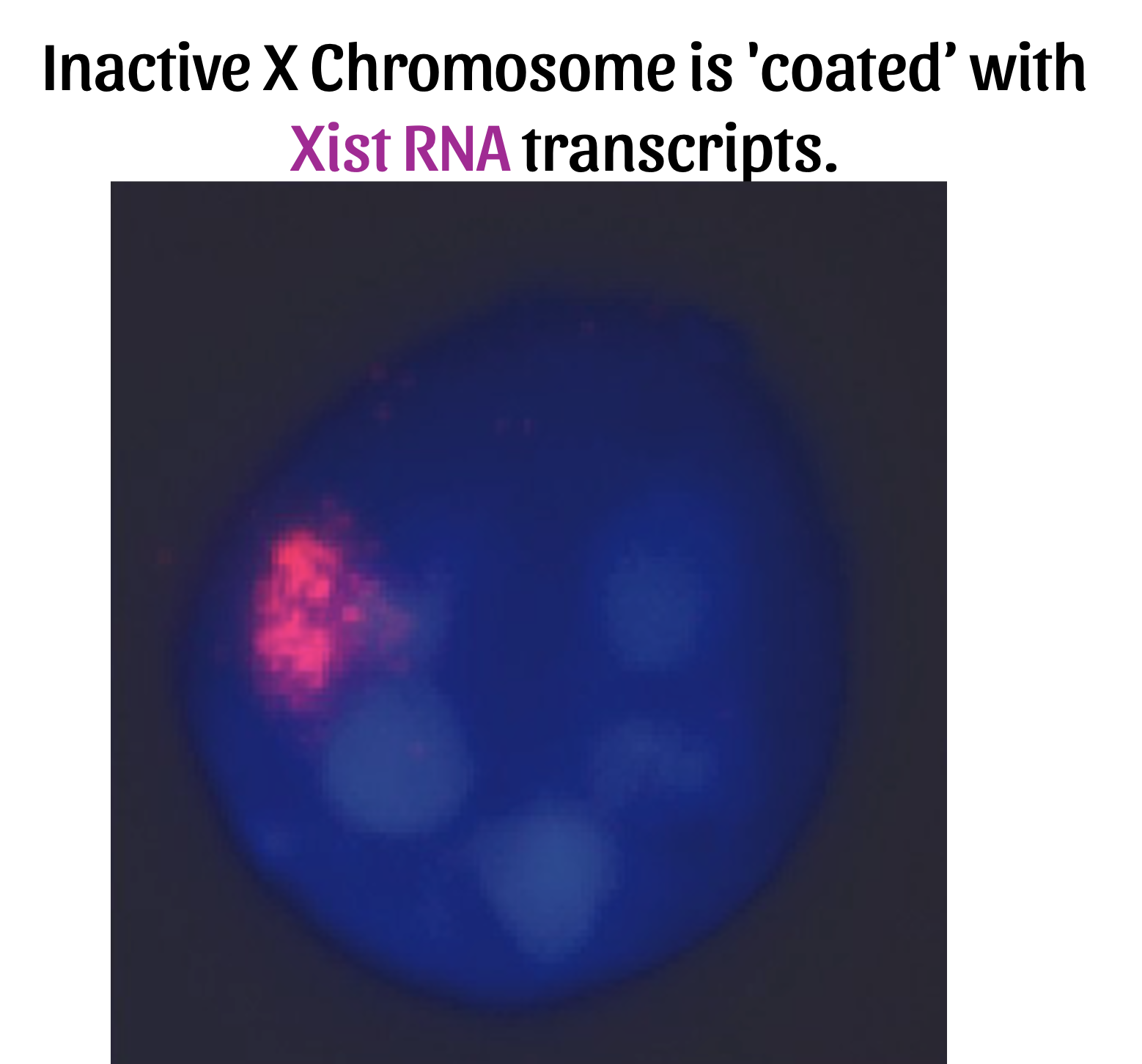
We are investigating how female lymphocytes maintain X-chromosome Inactivation (XCI), which is an epigenetic process responsible for equalizing gene expression between sexes. X-chromosome Inactivation silences one X-chromosome in female cells, and this process is initiated and maintained by the long noncoding RNA Xist.
Lab Mission
To investigate the epigenetic regulatory mechanisms of the inactive X chromosome in immune cells that maintain transcriptional silencing of most genes while promoting X-linked gene expression of specific genes.
To determine the genetic and epigenetic contributions responsible for the female bias in autoimmune diseases such as lupus and scleroderma.
To investigate how X-linked gene expression contributes towards sex-biased disease outcomes following pathogen infections.
Listen to an interview with Dr. Anguera on NPR (February 2024): 4 out of 5 autoimmune disease patients are women, and scientists want to know why
Listen to Dr. Anguera on Radiolab (August 2021): The Unsilencing
Interested in Working with Us?
We are always seeking highly motivated students and post-doctoral fellows with an interest in:
Epigenetics, X-chromosome Inactivation
Immunology and female-biased autoimmune disorders
Long noncoding RNAs
Genetics
Bioinformatics
Interested post-doctoral candidates should inquire by filling out the form or emailing anguera@vet.upenn.edu.
Interested graduate students should visit the Cellular and Molecular Biology (CAMB) Graduate Program at UPenn or inquire by filling out the form or emailing anguera@vet.upenn.edu.
Website designed by Zowie Searcy